Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Multi-Gaussian analysis of a dipolar signal¶
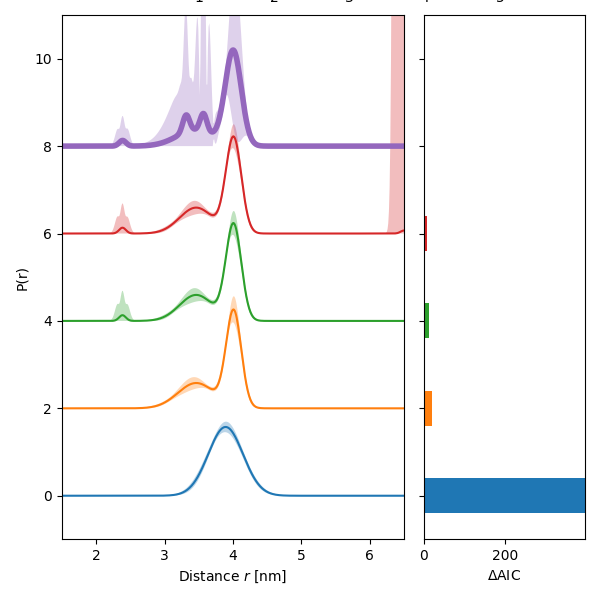
An example on how to perform a multi-Gauss analysis of dipolar signals using optimal selection of the number of components.
# Import the required libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.gridspec import GridSpec
from copy import deepcopy
import deerlab as dl
# File location
path = "../data/"
file = "example_4pdeer_1.DTA"
# Experimental parameters
tau1 = 0.3 # First inter-pulse delay, μs
tau2 = 4.0 # Second inter-pulse delay, μs
tmin = 0.1 # Start time, μs
# Load the experimental data
t, Vexp = dl.deerload(path + file)
# Pre-processing
Vexp = dl.correctphase(Vexp) # Phase correction
Vexp = Vexp / np.max(Vexp) # Rescaling (aesthetic)
t = t - t[0] # Account for zerotime
t = t + tmin
# Maximal number of Gaussians in the models
Nmax = 5
# Construct the distance axis
r = np.linspace(1.5, 6.5, 500)
# Pre-allocate the empty lists of models
Pmodels = [[] for _ in range(Nmax)]
Vmodels = [[] for _ in range(Nmax)]
# The basic model for the components (can be e.g. dl.dd_rice)
basisModel = deepcopy(dl.dd_gauss)
basisModel.mean.set(lb=min(r), ub=max(r), par0=3.5)
# Model construction
for n in range(Nmax):
# Construct the n-Gaussian model
Pmodels[n] = dl.lincombine(*[basisModel] * (n + 1))
# Construct the corresponding dipolar signal model
Vmodels[n] = dl.dipolarmodel(t, r, Pmodel=Pmodels[n])
# Fit the models to the data
fits = [[] for _ in range(Nmax)]
for n in range(Nmax):
fits[n] = dl.fit(Vmodels[n], Vexp, reg=False)
# Extract the values of the Akaike information criterion for each fit
aic = np.array([fit.stats["aic"] for fit in fits])
# Compute the relative difference in AIC
aic -= aic.min()
# Plotting
fig = plt.figure(figsize=[6, 6])
gs = GridSpec(1, 3, figure=fig)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, :-1])
for n in range(Nmax):
# Evaluate the n-Gaussian distance distribution model
Pfit = fits[n].evaluate(Pmodels[n], *[r] * (n + 1))
# Propagate the fit uncertainty to the model
Puq = fits[n].propagate(Pmodels[n], *[r] * (n + 1), lb=np.zeros_like(r))
# Calculate the 95%-confidence intervals
Pci = Puq.ci(95)
# Normalize the probability density functions
Pci /= np.trapezoid(Pfit, r)
Pfit /= np.trapezoid(Pfit, r)
# Plot the optimal fit with a thicker line
if n == np.argmin(aic):
lw = 4
else:
lw = 1.5
# Plot the distance distributions and their confidence bands
ax1.plot(r, n * 2 + Pfit, label=f"{1+n}", linewidth=lw)
ax1.fill_between(r, n * 2 + Pci[:, 0], n * 2 + Pci[:, 1], alpha=0.3)
# Plot the difference in AIC for each fit
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, -1])
for n in range(Nmax):
ax2.barh(2 * n, aic[n])
# Axes settings
ax1.set_ylabel("P(r)")
ax1.set_xlabel("Distance $r$ [nm]")
ax1.set_ylim([-1, 2 * Nmax + 1])
ax1.autoscale(enable=True, axis="x", tight=True)
ax2.set_xlabel("$\Delta$AIC")
ax2.set_ylim([-1, 2 * Nmax + 1])
ax2.autoscale(enable=True, axis="x", tight=True)
ax2.yaxis.set_ticklabels([])
# Legend settings
handles, labels = ax1.get_legend_handles_labels()
fig.legend(
handles,
labels,
title="N-Gaussian model",
frameon=False,
loc="upper center",
ncol=Nmax,
bbox_to_anchor=(0.55, 1.07),
)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 29.710 seconds)